Engineering Mechanics Statics is a branch of engineering mechanics that studies the behavior of stationary objects or objects in a state of equilibrium. This field focuses on analyzing forces and moments on a stationary or uniformly moving object.
In Engineering Mechanics Statics, fundamental concepts such as support reactions, vectors, forces, moments, stresses, strains, and equilibrium are used to analyze various mechanical structures such as bridges, buildings, and machines. The goal is to design efficient, safe, and stable structures and systems.
Engineering mechanics statics - Introduction
The basic engineering discipline is engineering mechanics, which describes the motions of bodies and the forces associated with these motions.
Engineering mechanics investigates the equilibrium of forces as well as the resulting components’ stresses and deformations. Based on characteristics such as strength, permissible stresses, or deformations, a component is designed by comparing the applied stress with the capacity to withstand stress. This requires that the stress on a component is less than its capacity to withstand stresses.
In conjunction with the basic fields of materials science and machine elements, engineering mechanics provides fundamental calculation methods for creating engineering designs. Consequently, engineering mechanics should be understood as a bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical implementation, without which an understanding and comprehensive analysis of complex technical systems would not be possible.
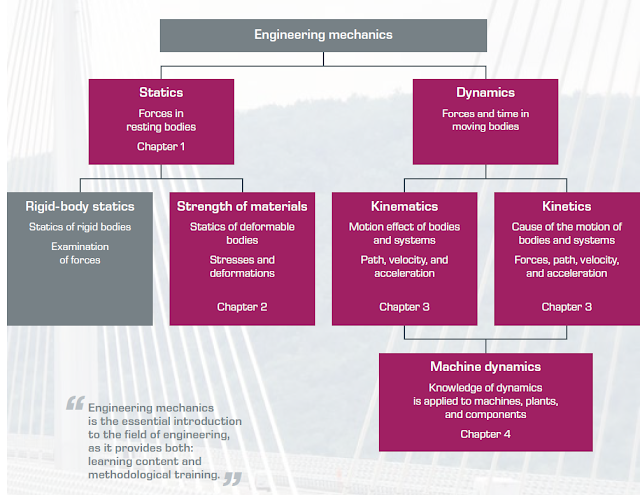
General classification of the discipline of engineering mechanics and placement in this catalogue
In universities, the discipline of engineering mechanics is usually divided into the following subdisciplines:
- engineering mechanics I, focusing on statics
- engineering mechanics II, focusing on strength of materials (elastostatics)
- engineering mechanics III, focusing on kinematics and kinetics (dynamics)
Topics in engineering mechanics
Statics courses include elementary knowledge for analysing loads on mechanical systems. This knowledge forms the basis for sizing and designing components and machine elements.
2. Strength of materials
Strength of materials deals with the deformation of elastic systems under loads such as pressure, tension, bending, torsion, and shearing as well as calculating the resulting stress states.
3. Dynamics (kinematics and kinetics)
Dynamics investigates moving systems. Kinematics deals with motion sequences without enquiring into the cause of motion. Kinetics looks at the motion of rigid bodies under the action of forces.
4. Machine dynamics
Building on the fundamentals of engineering mechanics, machine dynamics deals with the interaction between dynamic forces and motion quantities in machines.
Mau donasi lewat mana?
Donate with PaypalGopay-