Basic knowledge of Statics refers to the fundamental concepts and principles that are essential to understand the behavior of stationary objects or objects in a state of equilibrium. Some of the basic knowledge of Statics includes:
- Forces and Moments: The concept of force is fundamental to Statics. A force is a push or pull that is applied to an object. The moment of a force is the measure of its tendency to cause rotation.
- Equilibrium: In Statics, an object is said to be in equilibrium if it is not accelerating. For an object to be in equilibrium, the sum of all forces acting on the object must be zero and the sum of all moments must be zero.
- Supports and Reactions: A support is a structure that prevents the motion of an object in a particular direction. The reaction is the force that a support exerts on an object to prevent its motion.
- Structural Analysis: Structural analysis involves the study of the behavior of structures under different loads and conditions. This includes determining the forces acting on the structure and analyzing the deformation and stress caused by those forces.
- Friction: Friction is the force that opposes motion between two surfaces in contact. Friction plays an important role in Statics because it can cause a force to act in a different direction than intended.
Understanding these basic concepts is crucial to the study of Statics and the design of safe and efficient structures.
Basic knowledge Statics
Statics is the study of the effect of forces on rigid bodies, which are in equilibrium. Two forces are in equilibrium when they are equal, in opposing directions, and have the same line of action. In statics, a body is considered rigid when deformations, caused by acting forces, are negligibly small compared to the dimensions of the body
The main task of static analysis is to determine the equilibrium of the forces applied on a body or a mechanical system. Building on the axioms of mechanics, rigid-body mechanics deals with the equivalence and equilibrium of force systems, centre-of-gravity calculations, internal forces, and moments in beams and trusses along with problems on friction.
Generally, the field looks at supporting structures that are at rest and that must remain at rest owing to their function. Material properties are not considered in statics; these are covered by strength of materials.
Basic terms of statics
Force, as the cause of motion changes and/or deformations, is described by its magnitude, the position of the line of action, and direction along the line of action. Forces are divided according to different criteria:
Division by dimension
- Point force: only acts on a point (idealisation in mechanics)
- Linear force/line load: continuously distributed force along a line (idealisation in mechanics)
- Area force: affects only a specific area or is applied as a compressive load (water pressure on a dam, load of snow on a roof)
- Volume force: acts spatially distributed over the volume of a body (weight, magnetic and electrical forces)
Division by origin
Physical force or active force (F, q): acts in the normal direction on a body (e.g. weight, wind pressure and snow).
Reaction force or constraining force (AV, AH, BV): acts in the opposite direction to the physical force and causes the body to remain in equilibrium (e.g. normal force FN, support force and adhesive force).
Division in the system
Internal force: obtained by notionally cutting the body. This force acts between the parts of a body or system (normal force N, shear force Q and bending moment M).
External force: acts on a body from the outside (e.g. weight, wind pressure, snow load, adhesive force and support force)
Note:
- FG weight,
- q snow load,
- A and B support forces,
- index V vertical forces,
- index H horizontal forces,
- N normal force,
- Q shear force,
- M bending moment
Axioms of statics
Axiom of inertia:
Every body remains in a state of rest or uniform rectilinear motion unless it is compelled to change this state by the forces acting on it.
Axiom of displacement:
Two forces that are equal, have the same line of action and are in the same direction but different points of action, exert the same action on a rigid body, i.e. they are equivalent. In other words, the force vector can be displaced along the line of action.
Axiom of the parallelogram:
The action of two forces with a common point of action is equivalent to the action of a single force, whose vector is given as a diagonal in a parallelogram and which has the same point of action as the forces.
Axiom of reaction:
If a body exerts a force on a second body (action), this causes the second body to also exert a force on the first body (reaction), which is equal to the first force in magnitude and line of action, but which is in the opposite direction.
Experimental units for the field of statics
The engineering mechanics – statics chapter offers examples on the following subject areas:
Forces and moments
- demonstration of forces and graphical resolution of forces
- investigation of lever systems
- planar central force systems and statically defined systems
- bar forces, support forces, equilibrium of forces, equilibrium of moments and equilibrium conditions
 |
| Resolution of forces on the planar central force system |
Note:
- F1 and F2 bar forces
- FG weight
Internal reactions and methods of section
- demonstration of internal reactions
- application of the method of sections
- investigation of normal force, shear force and bending moment diagrams
 |
| shear force & bending moment diagrams |
 |
| Internal reactions in a beam |
Note:
- F external force,
- AV, AH, BV support forces,
- Q shear force,
- M bending moment
- bar forces in statically determinate and indeterminate trusses
- dependence of bar forces on external forces
- method of sections: method of joints and Ritter’s method
- graphical method: Cremona diagram
 |
Forces in various single plane trusses |
 |
| Method of joints to determining the forces on a truss |
Note:
- F force,
- FAx, FAy, FBy support forces,
- S bar forces,
- A-H joints
Bridges, beams, arches and cables
- calculation of support forces
- determining internal reactions
- different load cases: point load, line load and moving load
 |
| Parabolic arch |
 |
| Line load and support reactions on an arch |
- FAx, FAy, FBx, FBy support forces,
- q0 line load
Static and kinetic friction
- static and dynamic friction
- demonstration of frictional forces
- determining the coefficients of friction
 |
| Friction on the inclined plane |
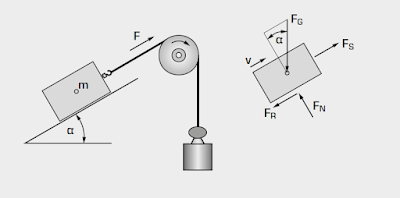 |
| Friction on the inclined plane |
- FG weight,
- FS external force,
- FN normal force,
- FR dynamic friction force, v velocity,
- α angle of inclination,
- m mass
Mau donasi lewat mana?
Donate with PaypalGopay-